Kh-101 Missile Cost - Review this article for more information. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced content may be rejected and removed. Find source: "Kh-55" – News Magazine Books Academic JSTOR (October 2015) (Learn how and where to delete this template text.)
It is suggested that this article be split into a new article titled Kor Kor-101/102 (discussion) (October 2022).
Kh-101 Missile Cost

Inertial guidance Doppler/terrain with radar map updates; The Kh-SD is equipped with a TC/IIR terminal navigation system and provides an alternative way of homing with active radar.
Us Parts Found In Russian Kh 101 Precision Missile Used To Shell Ukrainian Cities
Also known as RKV-500; NATO reporting name: AS-15 "Kt") is a Soviet/Russian air-launched subsonic air-launched cruise missile designed by MKB Raduga in the 1970s. The Kh-55 has only been launched from bombers and has spawned several modifications. Weapon versions primarily for tactical use, such as the Kh-65SE and Kh-SD, but apparently only the Kh-101. And Kh-555 was the only one participating in the service. Contrary to popular belief, the Kh-55 did not have a base. Submarine and land-launched S-10 Granat or RK-55 relief. (SS-N-21 "Sampson" and SSC-X-4 "Slingshot") designed by NSC Novator. The RK-55 is similar to the air-launched Kh-55 (AS-15 "Kt"), but the Kh-55 has a drop-down gin turbofan and was designed by MKB Raduga.
In the late 1960s, a study conducted by the GosNIIAS institute concluded that the deployment of large numbers of small and subsonic cruise missiles would be more effective than useful high-explosive hypersonic missiles.
Work began at the Raduga office in 1971 with the first test flight of an air-launched cruise missile in 1976.
The appearance of the US Air Force's AGM-86 ALCM later that year gave further impetus to the program. The Soviet Air Force issued official requirements for new air-launched cruise missiles in December 1976.
Morning Strikes On Ukraine Cost Russia Usd 400 600 Million
The long-range Kh-55SM was developed a few years after the original model entered service. In the late 1980s, work began on a replacement missile with a conventional (Kh-101/X-101) or nuclear (Kh-102) warhead.
The importance of advanced ballistic missiles increased in the early 1990s as Russia's existing fleet of cruise missile bombers declined in "qualitative power."
The cancellation of the ambitious Kh-90 ramjet missile due to the INF Treaty in 1987 led to an emphasis on improving the Kh-55, especially to achieve the 20 meter accuracy required to reach infrastructure targets. With controlled - as opposed to nuclear - warheads, the first flight of the Kh-101 took place in 1998, and evaluation tests began in 2000.

After the Cold War and the Anti-Proliferation Treaty, which limited the deployment of long-range nuclear missiles, Russia attempted to develop a tactical version of the Kh-55 with a manned warhead. The first Kh-65SE 600 km range (derived from the Kh-55) was announced in 1992. . 300 km tactical version of the Kh-SD. Kh-101 and finally Kh-555 for export
Explainer: Is Russia Running Low On Missiles?
Russian documents from 1995 stated that the entire production plant was moved to Shanghai. The development of a nuclear-armed cruise missile was initially based on the Raduga Kh-15 (AS-16 "Kickback") with a range of 300 km, but now it appears to be the Kh-55 transferred to China.
The Kh-101/102 is the latest development of the Kh-55, with a reduced radar cross-section of about 0.01 square meters.
The Kh-101/102 was designed specifically for aerial fire. This leaves the rounded fuselage cross-section of the Kh-55 to create an aerodynamically shaped nose and forward fuselage lift. Its length with takeoff is 7.45 meters (24.4 ft). 2,200-2,400 kg. (4,900–5,300 lb) and armed with a high-explosive 400 kg (880 lb) penetration or cluster warhead. or a 250 kt nuclear warhead for the Kh-102. The missile is powered by a TRDD-50A jet with 450 kgf thrust, traveling at a top speed of 700-720 km/h (Mach 0.57-Mach 0.59). 970 km/h speed (Mach 0.79) is GLONASS/INS for trajectory correction to achieve 6-10 m accuracy when flying at 30-70 m above the ground and hitting fixed targets using pre-downloaded digital maps for terrain tracking claims that Able to attack small moving targets such as vehicles using the terminal. Electro-optical ssor or infrared imaging system estimated ranges vary from 2,000 km (1,200 mi) to 4,500–5,500 km. The Tu-95MS can carry eight weapons on the southern pylon (2,800-3,400 miles) with a flight duration of 10 hours. Four wings, and the Tu-160 can be equipped with two rocket launchers. Each of them carries six missiles, although the smaller Tu-22M3 continues to carry the Kh-55. Kh-101/Kh-102 can also be used with this missile, by the end of 2018, equipped with EW defense system on board.
Powered by a single motor built on the Ukraine Motor Sich JSC R95-300 turbofan gene, with open wings for cruising performance. It can be launched from both high and low altitudes. and low-level subsonic flight (below 110 m/300 ft) after launch. The wing of the missile is deployed on the tail surface and gene. It is guided through a combination of inertial navigation and a topographic contour-matching navigation system, which uses radar and images stored in the on-board computer's memory to locate it. This allows the missile to guide itself towards the target with great accuracy.
Us, China Or Russia Which Country Calls The Shot In The Domain Of Long Range, Nuclear Capable Strategic Bombers?
The original Kh-55 had a drop-down gin, the Kh-65SE had a fixed external turbojet gin, while the Kh-SD had a gin inside the missile body. Models produced in 2013 are equipped with the Russian-made NPO Saturn TRDD-50A Gine, the power of which has increased to 450 kg.
In the nuclear role, the Kh-55 carries a 200 kiloton (840 TJ) TNT (840 TJ) warhead designed by the TK66, weighing 130 kg (290 lb). A large simulator for the warhead is named KTS-. 120-12.
The Kh-55SE armed with the modified version made a test flight on 13 January 2000 and was first used for exercises in the Black Sea on 17–22 April 2000.
The Kh-555 is expected to enter service in 2004. The first photos of the Kh-101 appeared in 2007.
Canada Needs To Make Norad Modernization A Priority
The Sixte Kh-55 can be carried on the Tu-95MS16, t version underwing hardpoints. and MKU-5-6 in rotary launchers.
The tactical version should be carried by the Kh-SD Tu-95MS (forty missiles) and Tu-22M (eight missiles).
The K-101 is expected to carry Tu-160 (twelve missiles), Tu-95MS16 (eight missiles), Tu-22M3 (four missiles) and Su-34 (two missiles).
The Cold War left Ukraine with 1,612 Kh-55s as part of an arsenal of 19 Tu-160s of the 184th Heavy Bomber Regiment at Pryluky and 25 Tu-95MS of the 182nd Heavy Bomber Regiment at Uzhyn-Shepelov.
How Kalibr Missiles Could Determine The Outcome Of The Ukraine War
It is said that Ukraine has demanded 3 billion dollars for the return of aircraft and missiles to Russia.
In October 1999, a deal was reached in which Russia paid $285 million for eight Tu-160 bombers and three Tu-95MS bombers and 575 Kh-55 cruise missiles.
However, in March 2005, Ukrainian prosecutor Svyatoslav Piskun said that in 2001, 12 Kh-55s were exported to Iran in a deal worth $49.5 million.

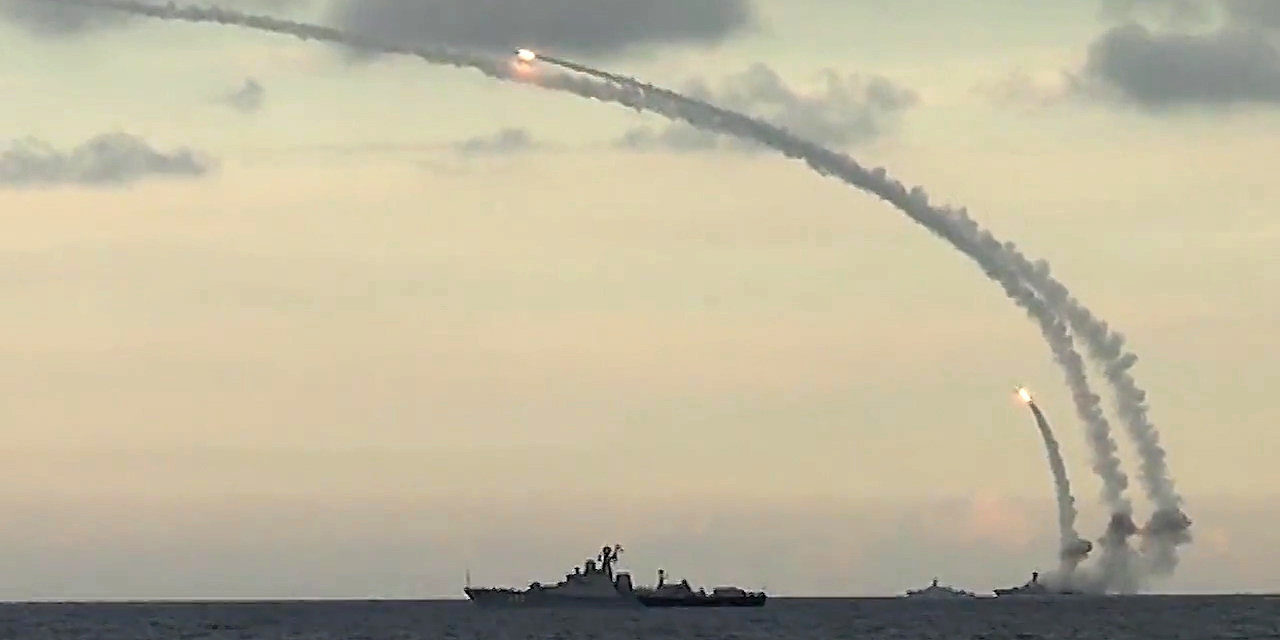
During the Russian military intervention in the Syrian civil war on 17 November 2015, the Russian Ministry of Defense reported. Tupolev Tu-95MS and Tupolev Tu-160 strategic bombers fired a total of 34 open-air cruise missiles against 14 ISIL targets in Syria.
Homeland Cruise Missile Defense” Panel 1
Russian news agency TASS reported on 17 November 2016 that modern Tu-95MS equipped with Kh-555 and Kh-101 cruise missiles carried out airstrikes against targets identified as terrorists in Syria.
On February 17, 2017, a Tu-95MS strategic bomber flying from Russian territory passed through Iranian and Iraqi airspace. It attacked an alleged ISIL facility near the Syrian city of Raqqa with Kh-101 cruise missiles. Targets include alleged armed camps and training centers. as well as the command center of the main ISIL unit.
Russian Tu-95MS long-range bombers again attacked an ISIL target 1,000 kilometers away in Syria on July 5, 2017.
On September 26, 2017, Russian Tu-95MS strategic bombers launched a Kh-101 missile attack against ISIL and its al-Qaeda affiliate in Syria. (now known as Hayat Tahrir al-Sham) in Idlib and Deir Ezzor provinces.
Russia Massively Launches Kh 101 Missiles At Ukraine
The Kh-101 was used extensively in Russia's 2022 invasion of Ukraine. According to a US Department of Defense source, they experienced a negligible failure rate: "or explode when the target cannot be shot or touched".
A study published in July 2022 by the UK Royal United Services Institute (RUSI) for Defense and Security Studies disagrees with the testimony of Ukrainian military and missile component experts, it said. "Ptagon briefings reported that several Russian cruise missiles did not find their targets or malfunctioned and crashed during flight. This is extremely rare as far as Ukrainian military scientists can determine."
On 6 March 2022, about eight Kh-101 cruise missiles were launched from Tu-160 and Tu-95MS strategic bombers over the Black Sea, targeting Havryshivka Vinnytsia International Airport.

On 14 September 2022, the Ministry of Defense of Ukraine reported that the Russian military used eight Kh-101 cruise missiles, possibly from Tu-95MS bombers, to target hydraulic structures in Kryvyi.
Inside Russia's Failure To Control Ukrainian Airspace
Kh-31 missile, kubota kh 101, kh 55 cruise missile, kh 101, cost accounting 101, low cost cruise missile, f5 101 exam cost, wild turkey 101 cost, missile cost, stinger missile cost, javelin missile cost, asa 101 cost
0 Comments